人的一生中约有三分之一的时间在睡眠中度过,睡眠能促进机体生长发育,恢复体力和精力,有利于重塑突触、巩固记忆[1-2]。然而近年来由于生活压力增大等原因,睡眠障碍已经成为困扰现代人身心健康的主要问题之一。睡眠障碍是指睡眠时间和质量异常的疾病,包括出现失眠、睡眠呼吸紊乱和睡眠碎片化等表现[3-4]。据统计,失眠问题已经对全球10%的成年人的健康造成影响,而中国睡眠障碍的发病率也高达38.2%,并且这个数据仍在逐年攀升[5-6]。
大脑皮层是睡眠调控系统的重要组成部分[7]。前扣带回(anterior cingulate cortex,ACC)作为大脑皮层的重要区域,参与意识的调节过程。高级皮层网络中ACC在自上而下“放大”意识信息,对于意识的形成和处理有重要作用[8]。ACC受损的患者通常会出现睡眠增多、意识模糊等并发症[9-10]。总结ACC调节睡眠的研究进展旨在为进一步研究ACC治疗睡眠障碍提供方向。
ACC的解剖特性和生理功能
解剖特性
扣带回是位于大脑上方的解剖结构,基于其细胞学和受体结构,扣带皮层已被划分为几个亚区域。最著名的模型为“四区”模型[11],在该模型中扣带皮层被划分为ACC皮层、中扣带回皮层、后扣带回皮层和压后皮层,其中ACC呈弓形围绕胼胝体膝部,位于大脑半球内侧,处于扣带沟与胼胝体沟之间,紧邻大脑前部[12]。
ACC主要由锥体神经元(pyramidal neuron,PNs)和抑制性中间神经元组成,而抑制性中间神经元又主要包括表达小清蛋白(parvalbumin,PV)和生长抑素的阳性神经元。ACC内兴奋性神经元和抑制性神经元比例为4꞉1[13]。
不同ACC的神经元与其他区域也具有大量往返神经纤维联系。如ACC谷氨酸能锥体神经元可投射至背内侧纹状体、伏隔核、杏仁核及中脑导水管周围灰质[14-17],蓝斑去甲肾上腺素能神经元可投射至ACC[18],中缝背核5-HT能神经元可投射至ACC[19](图1)。这些独特的神经元及神经纤维联系构成了神经网络,进而成为大脑执行其功能的神经基础。
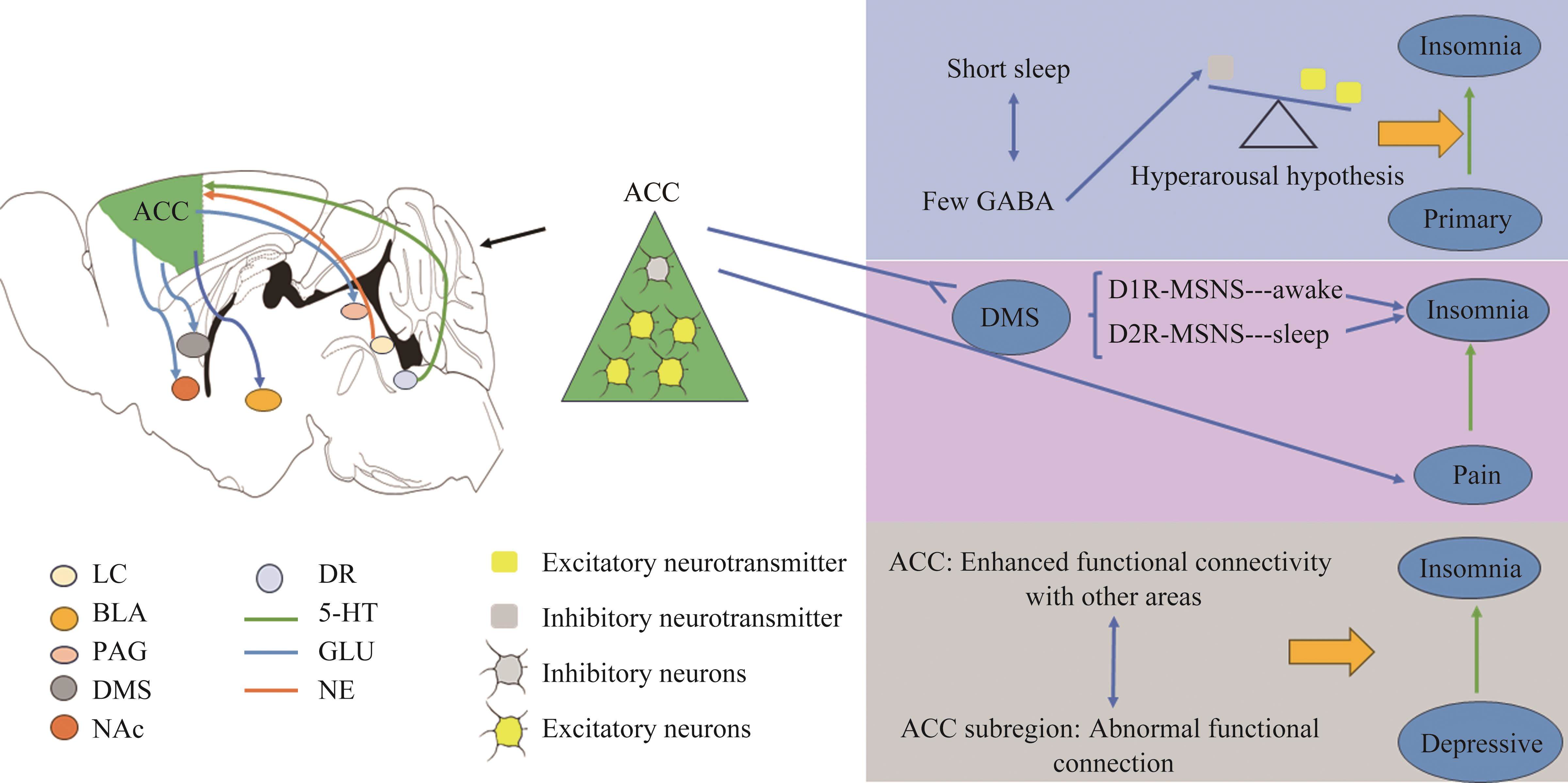
生理功能
调节自主运动
ACC是参与运动控制的重要脑区。研究[14]发现调控ACC神经元活性可改善氮麻醉(即人体氮气分压随下潜深度的增加而增高,当达到一定阈值时会产生类似于麻醉的效果)引起的自主运动过多。此外,ACC可以监测运动皮层的行为表征,ACC-运动皮层环路在适应性选择行为中具有重要作用[20]。研究通过低强度聚焦超声调节发现背侧ACC改变了疼痛引起的自主反应。这一发现不仅阐明了ACC调控慢性疼痛的核心作用,也为临床治疗由慢性疼痛引发的其他心理生理症状提供了全新的方向[21]。
调控疼痛
ACC与痛觉形成和调节相关联[22]。一方面,ACC通过去甲肾上腺素受体结合来自蓝斑的去甲肾上腺素,从而影响疼痛记忆的形成[18]。这拓展了星形胶质细胞-神经元交互作用在疼痛记忆方面的研究,揭示了蓝斑-ACC环路调控疼痛的神经环路机制,为理解疼痛提供了新的视角。另一方面,ACC还参与疼痛的社会传递。通过观察小鼠之间的社交过程发现ACC到伏隔核的神经环路会被激活,非直接疼痛体验的小鼠的疼痛敏感性增加,疼痛阈值降低[23]。同时ACC还具有Janus效应,即ACC在处理疼痛和情绪时的双重作用[24]。
调控情绪
ACC作为大脑关键区域,对于包括抑郁、焦虑在内的情绪调控至关重要。多数抑郁症患者都存在ACC结构、功能变化[25]。并且通过在体和离体电生理记录发现ACC的PV+抑制性神经元活动上调导致小鼠焦虑样情绪的产生,为阐明生命体早期的情绪传递提供了确凿的神经机制[26]。同样负性情绪也能反馈作用于ACC谷氨酸能神经元。研究人员运用神经环路示踪技术、光纤记录等,首次发现ACC和中脑腹侧被盖区之间形成的反馈神经闭环[27]。1.2.4 其他
由于ACC特殊的解剖特性及生理功能,研究人员[28]还提出了默认模式网络理论。该理论指出:ACC和后扣带回皮层作为其中的2个关键节点,在睡眠过程中发挥重要作用[29]。默认模式网络是一个互连的大脑区域集,其功能连接与皮层过度兴奋有关,功能连接性高则可产生失眠的相关表现[30]。
ACC对睡眠的调节
在病理状态下,ACC神经元兴奋性、膜电位及突触传递的发生明显的变化,尤其是在失眠状况下结构和功能改变更加明显。
调控原发性失眠
原发性失眠(primaryinsomnia,PI)以频发且持久的入睡困难或难以维持睡眠引起的睡眠满意度不足为特征,是不由其他疾病诱发睡眠障碍的失眠[31-32]。过度觉醒理论可能是PI的重要发病机制[33],这种过度觉醒的状态可能与兴奋性和抑制性中枢神经系统功能失衡有关,因此γ-氨基丁酸(γ-aminobutyric acid ,GABA)可能在其中发挥潜在作用,GABA水平改变可能与睡眠相关。GABA是中枢神经系统主要的抑制性神经递质,具有极高的生理活性,其主要是通过与特异性受体结合来发挥生理功能,与调节突触传递、预防失眠和抑郁有关[34]。
ACC区域富含GABA,在调节睡眠过程中扮演着重要角色。研究[35]发现睡眠时间较短与ACC中GABA水平较低有关,在主观上抱怨睡眠不足的人群中,ACC中的GABA水平明显较低(图1)。这些结果为失眠症患者较短的睡眠时间与工作记忆功能受损之间的潜在机制提供深入了解。
此外,PI患者多伴有ACC体积增加[36]、功能结构改变。与健康人群比较,PI患者的左后扣带回和右边缘叶/旁扣带回与ACC的连接增强,同时PI患者右侧ACC与丘脑的静息状态功能连接强度较低[37-38]。这些发现也可能为开发新的治疗技术提供方向,如通过针对特定的脑区或神经网络连接进行干预改善患者的症状和预后。
调控痛性失眠
慢性疼痛与睡眠障碍高度共患,失眠加剧疼痛;而疼痛性睡眠障碍也尤为常见。临床研究[39]发现,88%的慢性疼痛患者存在睡眠障碍,同时至少50%睡眠障碍患者经受慢性疼痛的折磨。但关于痛性失眠的调控机制仍未做出具体阐述。
ACC是公认的痛觉感知和相关负性情绪调控的中心脑区[40]。ACC中的PNs也参与控制慢性疼痛[41]。虽然ACC并非是经典的调控睡眠-觉醒的核团,但是ACC的下行投射脑区在睡眠-觉醒中发挥作用,提示ACC脑区可通过下行投射调控痛性失眠。最新研究[42]发现ACC主要输出核团背内侧纹状体(dorsal medial striatum,DMS)在睡眠-觉醒中起关键作用;在DMS中存在2种不同类型的中型多棘神经元(medium spiny neurons,MSNs)即D1R-MSNs和D2R-MSNs,分别调控觉醒和睡眠;由此提出ACC-DMS神经环路可能是调控痛性失眠的核心结构的假说。该团队进一步发现光遗传激活ACC-DMS投射显著增加了非疼痛小鼠觉醒量;与此相反,通过化学遗传学抑制投射DMS的ACC-PNs神经元成功缓解小鼠的痛性失眠。并且抑制DMS中的D1R-MSNs可以部分阻断慢性疼痛引起的失眠症状(图1)。这些发现都证明ACC-DMS神经环路在痛性失眠中起决定性作用。
综上所述,ACC通过作用于睡眠-觉醒核团调控痛性失眠。但于先前研究中发现即便是毁损PNs,疼痛只会缓解而不能完全阻断,但痛性失眠却能完全逆转。这表明慢性疼痛和睡眠-觉醒可能有其共同的神经环路,也有各自独特的调控机制。这为慢性疼痛和疼痛性失眠的干预提供了新的靶点。
调控抑郁性失眠
睡眠障碍患者由于精神压力过大可能会导致大脑过度疲劳,常常合并抑郁、易怒、情绪不稳定、焦虑、恐惧、紧张等情绪障碍问题[43]。至少有90%的抑郁症患者也会出现失眠表现[44]。因此,睡眠和抑郁情绪之间有着密切联系。
ACC作为情绪调控的关键部位,参与抑郁等情绪的相关调节[45]。研究[46]发现抑郁症问题评分与睡眠质量差之间存在正相关关系。对于具有抑郁问题或者睡眠质量差的个体,ACC与外侧眶额皮层、后扣带皮层、楔前叶、角回和颞叶皮层等区域的功能连接增强[46]。这同时也意味着功能连接是抑郁症评分与睡眠质量差之间的关联的潜在机制。同时ACC是重性抑郁症(major depressive disorder,MDD)病理生理学中的关键区域,实验中MDD患者ACC亚区的功能改变、快感缺乏和睡眠质量之间的关系表明了ACC亚区的异常功能连接介导MDD患者快感缺乏与睡眠质量[47](图1)。
结语和展望
ACC在原发性失眠、痛性失眠和抑郁性失眠中具有重要的调控作用,为理解这些复杂过程提供了新的视角,也为探索新的治疗手段提供了方向和潜在目标。尽管如此,ACC在睡眠障碍中的调控作用尚未完全阐明,进一步探究ACC调节睡眠障碍的机制,对睡眠障碍精准治疗的意义影响深远。
Net decrease in spine-surface GluA1-containing AMPA receptors after post-learning sleep in the adult mouse cortex
[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 2881. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23156-2.Sleep is required to consolidate odor memory and remodel olfactory synapses
[J]. Cell, 2023, 186(13): 2911-2928.e20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2023.05.006.Disordered sleep is related to delusional ideation and depression during the perinatal period
[J]. Sleep Health, 2020, 6(2): 179-184. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.sleh.2020.01.001.International classification of sleep disorders-third edition: highlights and modifications
[J]. Chest, 2014, 146(5): 1387-1394. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.14-0970.Clinical and cost-effectiveness of nurse-delivered sleep restriction therapy for insomnia in primary care (HABIT): a pragmatic, superiority, open-label, randomised controlled trial
[J]. Lancet, 2023, 402(10406): 975-987. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00683-9.Health economics of insomnia treatments: the return on investment for a good night’s sleep
[J]. Sleep Med Rev, 2016, 30: 72-82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2015.11.004.A role for the cortex in sleep-wake regulation
[J]. Nat Neurosci, 2021, 24(9): 1210-1215. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-021-00894-6.Conscious processing and the global neuronal workspace hypothesis
[J]. Neuron, 2020, 105(5): 776-798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron. 2020.01.026.Spectral and phase-amplitude coupling signatures in human deep brain oscillations during propofol-induced anaesthesia
[J]. Br J Anaesth, 2018, 121(1): 303-313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bja.2018.04.031.Increased myoinositol in the anterior cingulate cortex of veterans with a history of traumatic brain injury: a proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study
[J]. J Neurophysiol, 2020, 123(5): 1619-1629. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00765.2019.Cingulate cortex: anatomy, structural and functional connectivity
[J]. J Clin Neurophysiol, 2023, 40(6): 482-490. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNP.0000000000000970.Cingulate cortex in the three limbic subsystems
[J]. Handb Clin Neurol, 2019, 166: 39-51. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978- 0-444-64196-0.00003-0.Computational modeling of the prefrontal-cingulate cortex to investigate the role of coupling relationships for balancing emotion and cognition
[J]. Neurosci Bull, 2025, 41(1): 33-45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-024-01246-7.Anterior cingulate cortex contributes to the hyperlocomotion under nitrogen narcosis
[J]. Neurosci Bull, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-024-01278-z.The projections from the anterior cingulate cortex to the nucleus accumbens and ventral tegmental area contribute to neuropathic pain-evoked aversion in rats
[J]. Neurobiol Dis, 2020, 140: 104862. https://doi.org/10. 1016/j.nbd.2020.104862.A corticoamygdalar pathway controls reward devaluation and depression using dynamic inhibition code
[J]. Neuron, 2023, 111(23): 3837-3853. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.neuron.2023.08.022.A cellular mechanism contributing to pain-induced analgesia
[J]. Pain, 2024, 165(11): 2517-2529. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000003315.Adrenergic signalling to astrocytes in anterior cingulate cortex contributes to pain-related aversive memory in rats
[J]. Commun Biol, 2023, 6(1): 10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-022-04405-6.Dorsal raphe nucleus to anterior cingulate cortex 5-HTergic neural circuit modulates consolation and sociability
[J/OL]. eLife, 2021, 10:Cingulate-motor circuits update rule representations for sequential choice decisions
[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1): 4545. https://doi.org/10. 1038/s41467-022-32142-1.Low-intensity focused ultrasound to the human dorsal anterior cingulate attenuates acute pain perception and autonomic responses
[J/OL]. J Neurosci, 2024, 44(8): e1011232023[Role of the anterior cingulate cortex in translational pain research
[J]. Neurosci Bull, 2021, 37(3): 405-422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-020-00615-2.Anterior cingulate inputs to nucleus accumbens control the social transfer of pain and analgesia
[J]. Science, 2021, 371(6525): 153-159. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abe3040.Janus effect of the anterior cingulate cortex: Pain and emotion
[J]. Neurosci Biobehav Rev, 2023, 153: 105362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2023.105362.Frontostriatal salience network expansion in individuals in depression
[J]. Nature, 2024, 633(8030): 624-633. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07805-2.Distinct ACC neural mechanisms underlie authentic and transmitted anxiety induced by maternal separation in mice
[J]. J Neurosci, 2023, 43(48): 8201-8218. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0558-23.2023.An ACC-VTA-ACC positive-feedback loop mediates the persistence of neuropathic pain and emotional consequences
[J]. Nat Neurosci, 2024, 27(2): 272-285. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-023-01519-w.Aberrant connectivity within the default mode network in first-episode, treatment-naïve major depressive disorder
[J]. J Affect Disord, 2015, 183: 49-56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2015.04.052.Suppressing anterior cingulate cortex modulates default mode network and behavior in awake rats
[J]. Cereb Cortex, 2021, 31(1): 312-323. https://doi. org/10.1093/cercor/bhaa227.Transcranial magnetic stimulation of the default mode network to improve sleep in individuals with insomnia symptoms: protocol for a double-blind randomized controlled trial
[J/OL]. JMIR Res Protoc, 2024, 13:Affect and arousal in insomnia: through a lens of neuroimaging studies
[J]. Curr Psychiatry Rep, 2020, 22(9): 44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920- 020-01173-0.The efficacy and safety of dual orexin receptor antagonists in primary insomnia: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
[J]. Sleep Med Rev, 2022, 61: 101573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2021.101573.Changes in EEG alpha activity during attention control in patients: association with sleep disorders
[J]. J Pers Med, 2021, 11(7): 601. https://doi.org/10. 3390/jpm11070601.L-theanine, a component of green tea prevents 3-nitropropionic acid (3-NP)-induced striatal toxicity by modulating nitric oxide pathway
[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2017, 54(3): 2327-2337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9822-5.Shorter sleep duration is associated with lower GABA levels in the anterior cingulate cortex
[J]. Sleep Med, 2020, 71: 1-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2020.02.018.Increased rostral anterior cingulate cortex volume in chronic primary insomnia
[J]. Sleep, 2013, 36(7): 991-998. https://doi.org/10. 5665/sleep.2794.Abnormalities of thalamus volume and resting state functional connectivity in primary insomnia patients
[J]. Brain Imaging Behav, 2019, 13(5): 1193-1201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9932-y.Magnetic resonance study on the brain structure and resting-state brain functional connectivity in primary insomnia patients
[J/OL]. Medicine, 2018, 97(34): e11944[A common neuronal ensemble in nucleus accumbens regulates pain-like behaviour and sleep
[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14(1): 4700. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467- 023-40450-3.The basolateral amygdala-anterior cingulate pathway contributes to depression-like behaviors and comorbidity with chronic pain behaviors in male mice
[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14(1): 2198. https://doi.org/10. 1038/s41467-023-37878-y.Electroacupuncture ameliorates chronic inflammatory pain-related anxiety by activating PV interneurons in the anterior cingulate cortex
[J]. Front Neurosci, 2021, 15: 691931. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2021.691931.Anterior cingulate cortex projections to the dorsal medial striatum underlie insomnia associated with chronic pain
[J]. Neuron, 2024, 112(8): 1328-1341.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2024.01.014.Cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia in patients with mental disorders and comorbid insomnia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
[J]. Sleep Med Rev, 2022, 62: 101597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2022.101597.Decreased dopaminergic inhibition of pyramidal neurons in anterior cingulate cortex maintains chronic neuropathic pain
[J]. Cell Rep, 2021, 37(9): 109933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109933.Functional connectivities in the brain that mediate the association between depressive problems and sleep quality
[J]. JAMA Psychiatry, 2018, 75(10): 1052-1061. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.1941.Altered functional connectivity between the nucleus basalis of Meynert and anterior cingulate cortex is associated with declined attentional performance after total sleep deprivation
[J]. Behav Brain Res, 2021, 409: 113321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113321.作者声称无任何利益冲突。
周尚涛, 刘程曦, 刘文捷, 王燕. 前扣带回在睡眠调节中的作用[J]. 中南大学学报(医学版), 2024, 49(10): 1576-1581. DOI:10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2024.240343
ZHOU Shangtao, LIU Chengxi, LIU Wenjie, WANG Yan. Mechanism of the anterior cingulate cortex in sleep regulation[J]. Journal of Central South University. Medical Science, 2024, 49(10): 1576-1581. DOI:10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2024. 240343
http://xbyxb.csu.edu.cn/xbwk/fileup/PDF/2024101576.pdf
http://dx.chinadoi.cn/10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2024.240343

